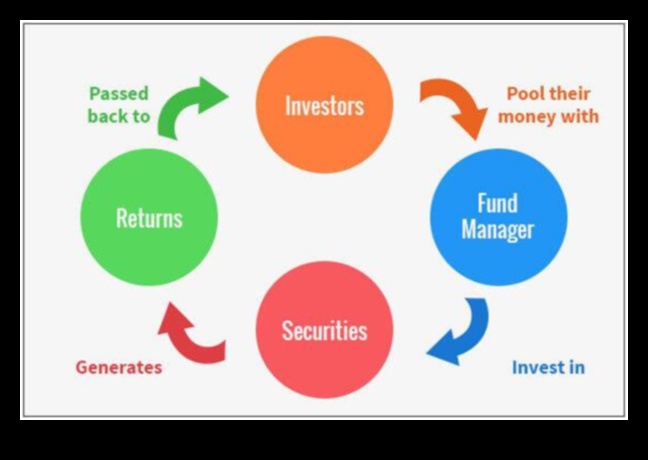
What is a Mutual Fund?
A mutual fund is a type of investment fund that pools money from multiple investors and invests it in a variety of stocks, bonds, and other securities. Mutual funds are often used by investors who want to diversify their portfolios and reduce risk.
How Do Mutual Funds Work?
When you invest in a mutual fund, you are essentially buying shares of the fund. The fund manager uses the money from investors to buy a variety of investments, such as stocks, bonds, and other securities. The value of your shares will go up or down depending on the performance of the underlying investments.
Types of Mutual Funds
There are many different types of mutual funds, each with its own investment objective and risk profile. Some of the most common types of mutual funds include:
- Stock funds invest in stocks of companies.
- Bond funds invest in bonds issued by governments or corporations.
- Money market funds invest in short-term debt securities.
- Index funds track the performance of a particular index, such as the S&P 500.
- Target-date funds are designed to reach a certain target date, such as retirement.
How to Choose a Mutual Fund
There are a few things to consider when choosing a mutual fund. These include your investment goals, risk tolerance, and time horizon. You should also consider the fees and expenses associated with the fund.
How to Invest in a Mutual Fund
You can invest in a mutual fund through a brokerage account. You can either buy shares directly from the fund company or through a broker.
Mutual Fund Fees and Expenses
Mutual funds charge a variety of fees, including:
- Management fees
- Distribution fees
- Redemption fees
It is important to understand the fees associated with a mutual fund before you invest.
The performance of a mutual fund is measured by its return, which is the annualized rate of growth of its share price. Mutual fund returns can vary significantly from year to year.
Mutual funds are taxed as ordinary income. This means that you will pay taxes on your mutual fund earnings each year, even if you do not withdraw the money from the fund.
There are a number of risks associated with investing in mutual funds, including:
- Market risk
- Interest rate risk
- Currency risk
- Liquidity risk
It is important to understand the risks associated with mutual funds before you invest.
- What is the difference between a mutual fund and an ETF?
- How do I know if a mutual fund is right for me?
- How much money do I need to invest in a mutual fund?
- How often should I rebalance my mutual fund portfolio?
| Feature | Mutual Fund | Investment | Diversification | Risk | Return |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Definition | A mutual fund is a type of investment vehicle that pools money from multiple investors and invests it in a variety of stocks, bonds, and other securities. | Pooling money allows investors to access a wider range of investments than they would be able to afford on their own. | By investing in a variety of assets, mutual funds can help to reduce risk. | The risk of a mutual fund depends on the types of investments it holds. | Mutual funds can provide a higher return than other types of investments, but there is no guarantee of a positive return. |
| Types | There are many different types of mutual funds, each with its own unique investment objective. | Some common types of mutual funds include: | • Stock funds | • Bond funds | • Balanced funds |
| How to choose | There are a few things to consider when choosing a mutual fund, including your investment goals, risk tolerance, and time horizon. | You should also consider the fees and expenses associated with a mutual fund. | It is important to do your research before investing in a mutual fund to make sure that it is a good fit for your needs. | The return on a mutual fund depends on the performance of the underlying investments. | There is no guarantee of a positive return on any investment, including mutual funds. |
| How to invest | You can invest in a mutual fund through a brokerage account. | When you invest in a mutual fund, you are buying shares of the fund. | The price of a mutual fund share is based on the value of the underlying investments. | The risk of a mutual fund can change over time, depending on the performance of the underlying investments. | The return on a mutual fund can also change over time, depending on the performance of the underlying investments. |
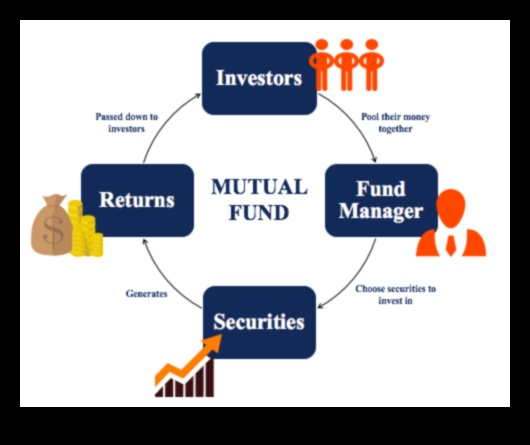
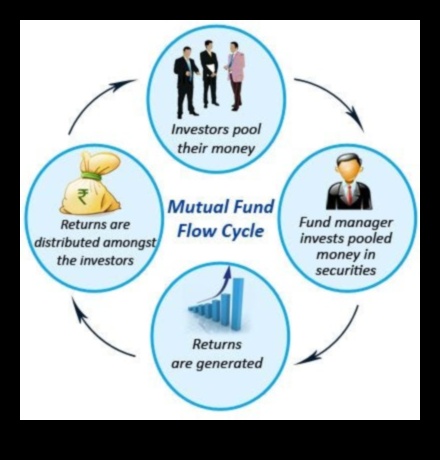
II. How Do Mutual Funds Work?
Mutual funds pool the money of many investors and invest it in a variety of stocks, bonds, and other securities. This diversification helps to spread out risk and can potentially lead to higher returns than investing in individual stocks or bonds.
Mutual funds are typically managed by professional investment managers who are responsible for making investment decisions on behalf of the fund’s shareholders.
There are many different types of mutual funds, each with its own unique investment objective and strategy. Some of the most common types of mutual funds include:
- Stock funds
- Bond funds
- Index funds
- Target-date funds
- Exchange-traded funds (ETFs)
When choosing a mutual fund, it is important to consider your investment goals, risk tolerance, and time horizon.
Mutual funds can be a great way to invest for retirement, college savings, or other long-term goals. However, it is important to remember that mutual funds are not without risk. There is always the possibility of losing money when investing in mutual funds.
III. Types of Mutual Funds
There are many different types of mutual funds, each with its own unique investment objective and strategy. Some of the most common types of mutual funds include:
- Stock funds
- Bond funds
- Money market funds
- Index funds
- Target-date funds
- Exchange-traded funds (ETFs)
Each type of mutual fund has its own advantages and disadvantages, and the best type of fund for you will depend on your individual investment goals and risk tolerance.
For more information on the different types of mutual funds, please see our article on the different types of mutual funds.
What is a Mutual Fund?
A mutual fund is a type of investment vehicle that pools money from investors and invests it in a diversified portfolio of stocks, bonds, and other securities. Mutual funds are offered by investment companies, which act as the fund’s manager and oversee its investment activities.
Mutual funds offer a number of advantages over investing in individual stocks or bonds. For example, mutual funds provide diversification, which can help to reduce risk. They also offer professional management, which can help investors to make better investment decisions.
However, mutual funds also have some disadvantages. For example, mutual funds typically charge fees, which can eat into your returns. Additionally, mutual funds may not be as liquid as investing in individual stocks or bonds.
Overall, mutual funds can be a good investment option for investors who are looking for a diversified, professionally managed investment. However, it is important to understand the risks and fees associated with mutual funds before investing.
How to Invest in a Mutual Fund
Mutual funds are a great way to invest for your retirement or other long-term goals. They offer diversification, professional management, and low costs.
To invest in a mutual fund, you can either open an account with a brokerage firm or use a robo-advisor.
Once you have an account, you can choose the mutual funds you want to invest in. You can choose from a variety of funds, including stock funds, bond funds, and money market funds.
To make a purchase, you will need to provide the brokerage firm with the amount of money you want to invest and the fund you want to invest in. The brokerage firm will then purchase shares of the fund for you.
You can also sell your shares of a mutual fund at any time. However, you may have to pay a fee if you sell your shares within a certain period of time.
Mutual funds are a great way to invest for your long-term goals. They offer diversification, professional management, and low costs. If you are looking for a way to invest for your retirement or other long-term goals, consider investing in a mutual fund.
VI. Mutual Fund Fees and Expenses
Mutual funds charge a variety of fees and expenses, including:
- Management fees
- Distribution fees
- Redemption fees
- Trading costs
- Other fees
These fees can eat into your returns, so it’s important to understand them before you invest in a mutual fund.
Management fees are paid to the fund’s investment manager. They typically range from 0.5% to 2.0% of the fund’s assets under management.
Distribution fees are paid to the fund’s distributor. They are typically used to cover the costs of marketing and selling the fund.
Redemption fees are charged when you sell your shares of a mutual fund. They are typically a percentage of the amount you sell.
Trading costs are incurred when the fund manager buys and sells stocks and other investments. These costs can include brokerage commissions, bid-ask spreads, and other fees.
Other fees can include things like legal fees, audit fees, and custodian fees.
It’s important to read the fund’s prospectus carefully to understand all of the fees that you will be charged.
You can also compare the fees of different mutual funds to find the one with the lowest cost structure.
By understanding the fees and expenses of mutual funds, you can make informed decisions about which funds to invest in.
VII. Mutual Fund Performance
Mutual fund performance is an important factor to consider when choosing a fund. There are a number of factors that can affect a fund’s performance, including the following:
- The fund’s investment objective
- The fund’s asset allocation
- The fund’s manager
- The fund’s fees and expenses
- The market environment
It is important to note that past performance is not necessarily indicative of future results. However, a fund’s historical performance can provide some insight into its potential for future returns.
There are a number of ways to measure mutual fund performance. The most common measure is the return on investment (ROI), which is calculated by taking the fund’s total return over a period of time and dividing it by the initial investment. Other common measures of performance include the Sharpe ratio, the Treynor ratio, and the information ratio.
When evaluating a mutual fund’s performance, it is important to consider the fund’s overall risk-return profile. A fund with a high return may also have a high level of risk. It is important to find a fund that strikes a balance between risk and return that is appropriate for your investment goals.
Mutual fund performance is an important factor to consider when choosing a fund. However, it is important to remember that past performance is not necessarily indicative of future results. When evaluating a fund, it is important to consider the fund’s overall risk-return profile and to make sure that the fund is aligned with your investment goals.
Taxation of Mutual Funds
IX. Risks of Investing in Mutual Funds
There are a number of risks associated with investing in mutual funds, including:
- Market risk: The value of a mutual fund can go up or down, and you may lose money if you sell your shares when the value is low.
- Interest rate risk: If interest rates rise, the value of bonds in your mutual fund may decrease.
- Credit risk: If the companies or governments that issued the bonds in your mutual fund default on their debt, the value of your shares may decrease.
- Liquidity risk: You may not be able to sell your shares of a mutual fund quickly if you need to do so.
- Political risk: The value of your mutual fund may be affected by political events, such as changes in government policy or economic conditions.
It is important to be aware of these risks before you invest in a mutual fund. You should also make sure that the mutual fund is appropriate for your investment goals and risk tolerance.
IX. Risks of Investing in Mutual FundsMutual funds are generally considered to be a safe investment, but there are still some risks involved. These risks include:
- Market risk: The value of a mutual fund can go down as well as up. This is due to changes in the stock market, the bond market, or other financial markets.
- Interest rate risk: When interest rates rise, the value of bonds held by a mutual fund will decline. This can lead to losses for investors.
- Inflation risk: Inflation can erode the value of a mutual fund’s investments over time. This is because the prices of goods and services increase, which means that the value of a mutual fund’s investments will not keep pace with inflation.
- Liquidity risk: Some mutual funds may be difficult to sell quickly, which can lead to losses if the investor needs to sell the fund in a hurry.
- Diversification risk: A mutual fund that is not well-diversified may be exposed to more risk than a mutual fund that is well-diversified. This is because a poorly-diversified mutual fund may have a large exposure to a single asset class or security, which could lead to large losses if that asset class or security performs poorly.
It is important to be aware of these risks before investing in a mutual fund. By understanding the risks, investors can make informed decisions about which mutual funds to invest in and how much to invest.
X. FAQ
Q1: What is a mutual fund?
A mutual fund is a type of investment vehicle that pools money from multiple investors and invests it in a diversified portfolio of stocks, bonds, and other securities. Mutual funds offer investors a number of benefits, including diversification, professional management, and low costs.
Q2: How do mutual funds work?
When you invest in a mutual fund, you are essentially buying shares of the fund. The fund manager then uses your money to purchase a diversified portfolio of stocks, bonds, and other securities. The value of your shares will fluctuate based on the performance of the underlying investments.
Q3: What are the risks of investing in mutual funds?
There are a number of risks associated with investing in mutual funds, including market risk, interest rate risk, and inflation risk. It is important to understand these risks before investing in a mutual fund.