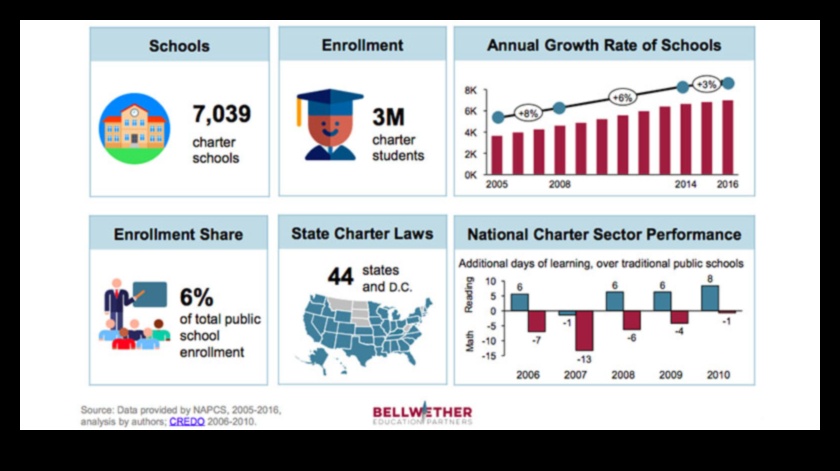
How are charter schools funded?
Charter schools are public schools that operate independently of the local school district. They receive funding from a variety of sources, including the state government, local school districts, and private donors.
The amount of funding that a charter school receives depends on a number of factors, including the size of the school, the number of students enrolled, and the cost of living in the area.
Charter schools are typically funded at a lower level than traditional public schools. This is because they are not required to provide the same level of services as traditional public schools. For example, charter schools are not required to offer sports teams or music programs.
The lower level of funding that charter schools receive has been a source of controversy. Some people argue that charter schools are not being given a fair chance to succeed. Others argue that charter schools should be held to the same standards as traditional public schools and that they should receive the same level of funding.
The debate over charter school funding is likely to continue for some time. In the meantime, charter schools will continue to operate on a shoestring budget.
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Charter school funding | The sources of funding for charter schools |
| Charter school finance | The financial management of charter schools |
| Charter school revenue | The sources of revenue for charter schools |
| Charter school budget | The budget of charter schools |
| Charter school money | The financial resources of charter schools |
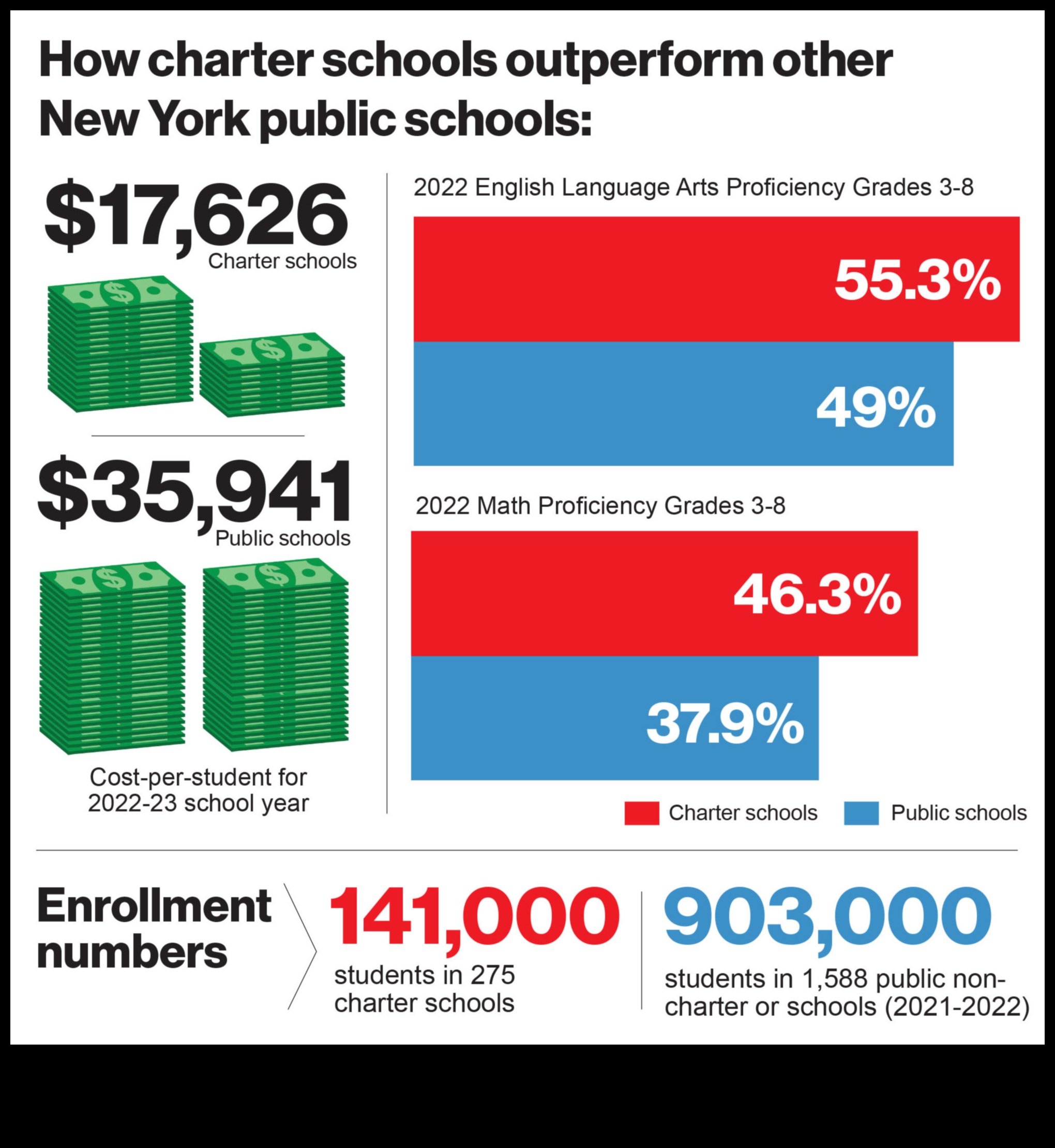
II. What is charter school funding?
Charter school funding is the money that is used to support the operations of charter schools. There are a variety of sources of charter school funding, including state and local government funds, private donations, and student tuition. The amount of funding that a charter school receives depends on a number of factors, such as its location, its size, and its student population.
III. Sources of charter school funding
There are a variety of sources of funding for charter schools, including:
- Government funding
- Private donations
- Fundraising
- Student fees
- Other sources
Government funding is the most common source of funding for charter schools, and it comes from a variety of sources, including state and federal grants, as well as local property taxes. Private donations are another important source of funding for charter schools, and they can come from individuals, foundations, and corporations. Fundraising is also a common way for charter schools to raise money, and they often hold events such as bake sales, car washes, and 5K runs. Student fees are another source of funding for charter schools, and they are typically charged to students who attend the school. Other sources of funding for charter schools include income from investments, rent from leased property, and grants from non-profit organizations.
III. Sources of charter school funding
There are a variety of sources of funding for charter schools, including:
- Government funding
- Private donations
- Fundraising
- Student fees
- Other sources
Government funding is the most common source of funding for charter schools, and it comes from a variety of sources, including:
- Federal funding
- State funding
- Local funding
Private donations are another important source of funding for charter schools, and they can come from a variety of sources, including:
- Philanthropic foundations
- Individual donors
- Corporations
Fundraising is another way that charter schools can raise money, and they can do this in a variety of ways, including:
- Holding events
- Selling merchandise
- Applying for grants
Student fees are another source of funding for charter schools, and they can charge students a variety of fees, including:
- Tuition
- Enrollment fees
- Book fees
Finally, there are a variety of other sources of funding that charter schools can access, including:
- Earned income
- Investments
- Licensing fees
The specific sources of funding that a charter school can access will vary depending on the state in which it is located.
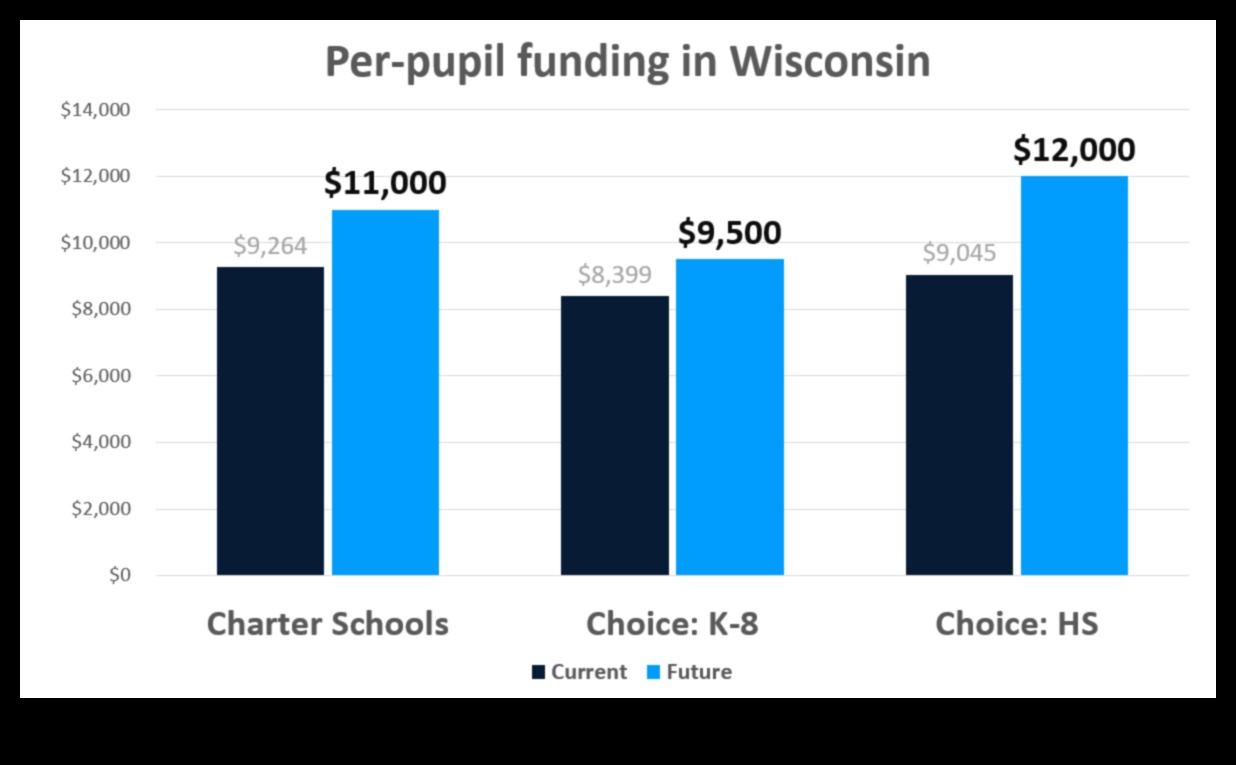
V. How are charter schools funded in different states?
The funding of charter schools varies significantly from state to state. Some states provide a significant amount of funding for charter schools, while others provide very little. In general, states that provide more funding for charter schools tend to have more charter schools.
There are a number of factors that contribute to the variation in charter school funding from state to state. These factors include:
- The political climate in the state
- The state’s education funding formula
- The state’s charter school law
- The state’s economy
The political climate in the state is a major factor in determining how much funding is available for charter schools. In states where there is strong support for charter schools, there is more likely to be a political will to provide funding for them.
The state’s education funding formula is another important factor in determining how much funding is available for charter schools. In states where the education funding formula is based on enrollment, charter schools receive a smaller share of funding than traditional public schools. This is because charter schools typically have fewer students than traditional public schools.
The state’s charter school law also plays a role in determining how much funding is available for charter schools. In states where the charter school law is more restrictive, charter schools receive a smaller share of funding than traditional public schools. This is because restrictive charter school laws make it more difficult for charter schools to open and operate.
The state’s economy is another factor that can affect the amount of funding available for charter schools. In states with strong economies, there is more likely to be a financial surplus that can be used to fund charter schools.
The variation in charter school funding from state to state has a number of implications. First, it means that charter schools in some states have more resources than charter schools in other states. This can lead to disparities in the quality of education that charter school students receive. Second, it makes it difficult for charter schools to operate across state lines. If a charter school is located in a state with low funding, it may not be able to afford to open a branch in a state with higher funding.
The variation in charter school funding is a complex issue with no easy solutions. However, it is an important issue that policymakers need to consider as they make decisions about the future of charter schools.
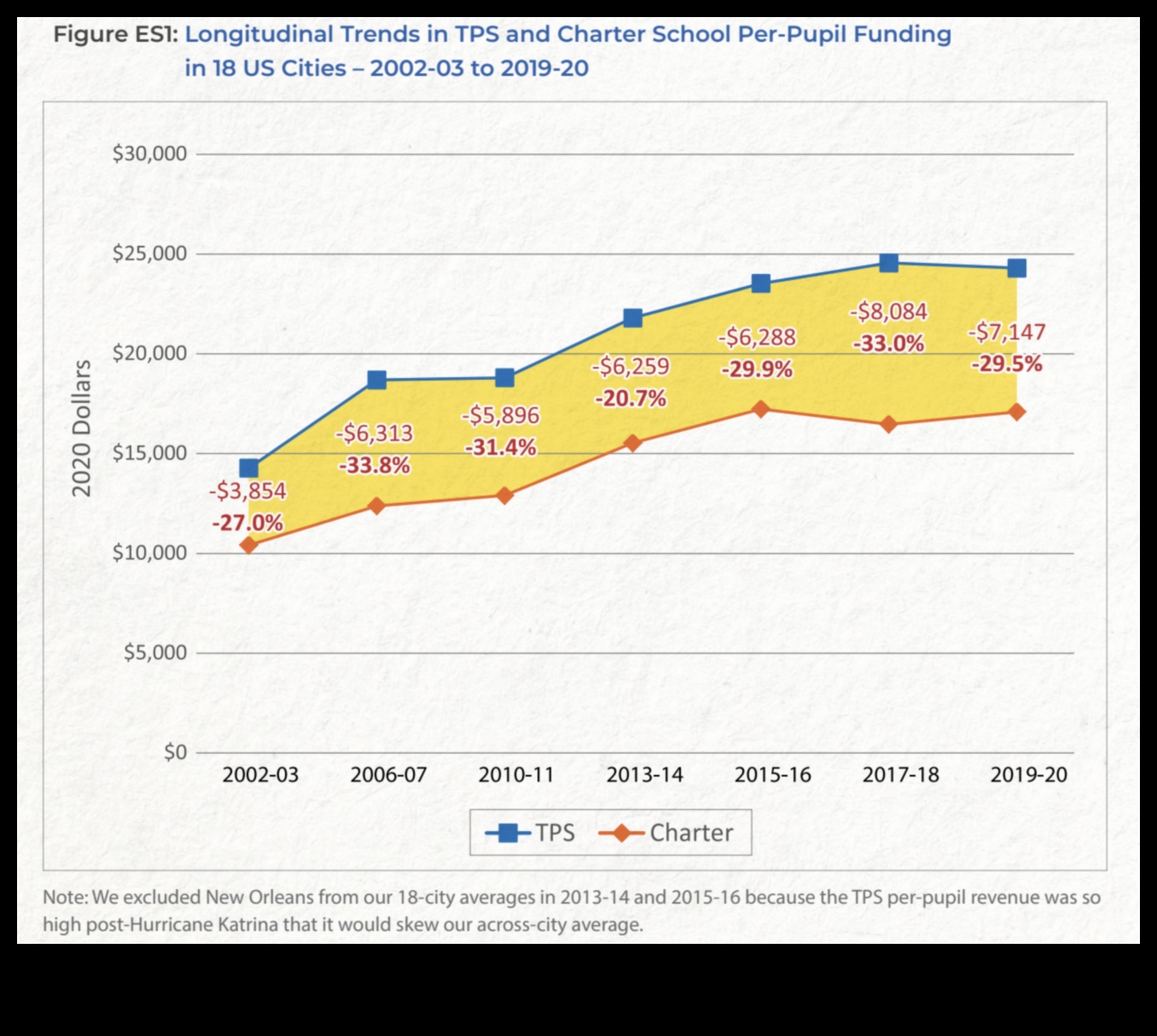
How are charter schools funded?
Charter schools are public schools that operate independently of the local school district. They receive funding from a variety of sources, including the state government, local school districts, and private donors.
The amount of funding that charter schools receive varies from state to state. In general, charter schools receive less funding per student than traditional public schools. This is because charter schools are not required to provide the same level of services as traditional public schools.
Charter schools use their funding to cover a variety of expenses, including teacher salaries, student supplies, and school operations. They may also use their funding to offer innovative programs and services that are not available at traditional public schools.
The challenges that charter schools face in terms of funding include:
- The lack of a consistent funding formula
- The need to raise private funds
- The need to compete for students with traditional public schools
Despite these challenges, charter schools have been shown to be a successful educational option for many students. They offer a variety of innovative programs and services that can help students to succeed in school.

VII. The future of charter school funding
The future of charter school funding is uncertain. There are a number of factors that could affect the amount of funding that charter schools receive, including the political climate, the economy, and the changing needs of students.
One of the biggest challenges facing charter schools is the fact that they are often underfunded. This is due to a number of factors, including the fact that charter schools are not eligible for the same level of funding as traditional public schools. This lack of funding can make it difficult for charter schools to provide the same level of services as traditional public schools.
Another challenge facing charter schools is the fact that they are often seen as a threat to traditional public schools. This is because charter schools can take away students and funding from traditional public schools. This can lead to resentment and hostility between charter schools and traditional public schools.
Despite these challenges, there are also a number of factors that could lead to an increase in funding for charter schools. For example, there is a growing demand for charter schools from parents who are looking for more choice and innovation in their children’s education. Additionally, there is a growing recognition that charter schools can be a valuable tool for improving the quality of education for all students.
The future of charter school funding is likely to be shaped by a number of factors, including the political climate, the economy, and the changing needs of students. It is important to remember that charter schools are a relatively new phenomenon, and their funding is still evolving. It is likely that the debate over charter school funding will continue for many years to come.
FAQ
This section answers some of the most common questions about charter school funding.
-
What are the different sources of funding for charter schools?
-
How much funding do charter schools receive?
-
How is the funding used?
-
What are the challenges that charter schools face in terms of funding?
In this article, we have discussed the different sources of funding for charter schools, how much funding charter schools receive, and how the funding is used. We have also discussed the challenges that charter schools face in terms of funding.
Overall, charter schools are funded through a variety of sources, including state and local government funding, private donations, and tuition. The amount of funding that charter schools receive varies depending on the state and the type of charter school. Charter schools typically use their funding to cover the costs of operations, such as teacher salaries, curriculum, and facilities.
The challenges that charter schools face in terms of funding include the need to raise private donations, the need to compete with public schools for students, and the need to meet the requirements of state and local governments. Despite these challenges, charter schools continue to grow in popularity and are seen as a viable option for providing high-quality education to students.
FAQ
Q: What are the different sources of funding for charter schools?
A: There are three main sources of funding for charter schools:
State and local government funding. Charter schools receive funding from the state and local governments in the same way that traditional public schools do. This funding is based on the number of students enrolled in the school.
Private donations. Charter schools can also receive funding from private donors, such as foundations, corporations, and individuals. This funding can be used for a variety of purposes, such as teacher salaries, curriculum development, and school supplies.
Parent and student fees. Charter schools can charge parents and students fees to help cover the cost of operating the school. These fees can be used for a variety of purposes, such as teacher salaries, curriculum development, and school supplies.
Q: How much funding do charter schools receive?
A: The amount of funding that charter schools receive varies from state to state. In general, charter schools receive less funding per student than traditional public schools. This is because charter schools are not required to provide the same level of services as traditional public schools.
Q: How is the funding used?
A: Charter schools use their funding to provide a variety of educational services to their students. This funding can be used for teacher salaries, curriculum development, school supplies, and other educational expenses.
Q: What are the challenges that charter schools face in terms of funding?
A: Charter schools face a number of challenges in terms of funding. These challenges include:
Inadequate funding. Charter schools often receive less funding per student than traditional public schools. This can make it difficult for charter schools to provide the same level of services as traditional public schools.
Unpredictable funding. The amount of funding that charter schools receive can vary from year to year. This can make it difficult for charter schools to plan for the future.
Political challenges. Charter schools are often controversial, and they can face political opposition from traditional public schools and teachers’ unions. This opposition can make it difficult for charter schools to receive the funding that they need.